Shan State, Myanmar
Client Requirements
In developing something appropriate, the following considerations were important:
• Whilst extensive, the rural road network was poorly defined, with no road numbering or network referencing system in use. The ability to map the network would therefore be a significant advantage to road managers.
• The large size of the rural road network required data collection to be as quick as possible, in order to minimise its cost.
• The technical, staffing and financial capabilities of the road agency were very limited,especially at the local level, through whom data collection would be expected to be managed. This precluded the use of expensive or sophisticated systems, or any that required specialised equipment or high technology.
• The ability to store and process a large volume of data locally was limited.
• Most of the areas served by the rural road network had no or very limited mobile phone coverage.
• Access to the internet was slow, unreliable and/or expensive in many offices in local towns. This meant that it was not possible to provide remote access to a central server via the internet, and data transfers had to be kept small.
• Local security concerns meant that any collected data had to be stored locally and not offshore (thus, a ‘cloud’ based option was not acceptable).
System Overview
In response to these conditions, the RoadMark system was developed and piloted locally. As part of this project, just over 500km of rural roads were surveyed using the RoadMark smartphone app.
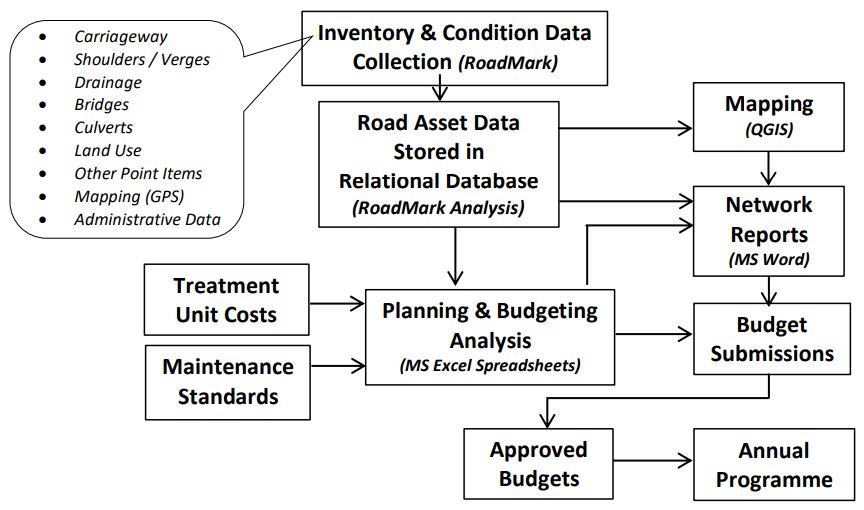
The data from these surveys was stored in a database using RoadMark Analysis (RMA) on a Windows10 computer. This data was then exported for subsequent analysis using a simple Excel spreadsheet, from which estimated network needs and budgets were derived. The data was also mapped using the freely available QGIS software. A summary of the overall system architecture is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Summary of Overall Planning & Budgeting Approach
Data Collection: RoadMark Android App
A dedicated application RoadMark was developed to allow a wide range of road asset data to be collected quickly using an Android Smartphone. This application
was designed to be used by non-technical inspectors, in areas that have no mobile or internet connections, on poorly defined road networks. RoadMark
allows basic inventory and condition data to be captured for each of the main types of road assets. All data is date and time stamped and geolocated,
allowing the data to be mapped subsequently.
Figure 2: Piloting Data Collection in Shan State

Note: A data collection team only requires two individuals:one data collector and one vehicle operator.
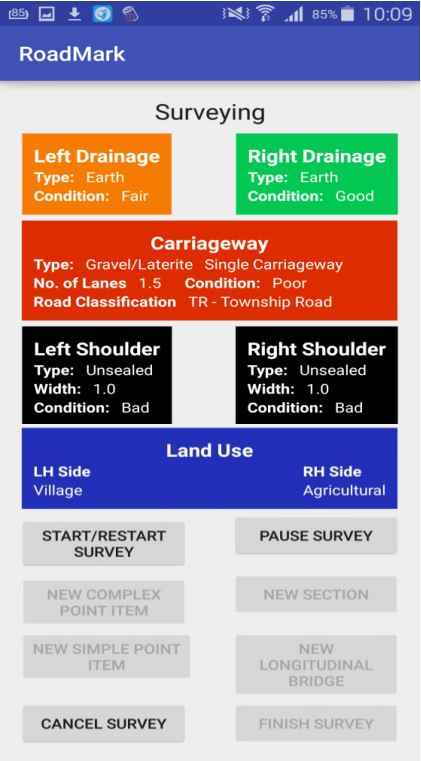
The main screen shown by the RoadMark Android app during surveying (see Figure 3) displays key attributes for each of the main components of the roadway (with changing colours, depending on condition). Additional options at the bottom of the form allow the surveyor to record extra details about ‘point items’ such as bridges, culverts, street furniture, intersection and so on. RoadMark can be used on poorly defined road networks, where no systematic referencing system has been established,(although it can accommodate this if present). The user can trigger a new section if there is a significant change in the road’s characteristics, such as a change of surface type, condition and/or administrative data (e.g. district name or road class).
The desktop application RoadMark Analysis calculates section lengths automatically, based on frequent GPS positions (accurate to within approximately 3m). It can then create sections within the database. Data is checked for logical consistency when entered into RoadMark. Additional checks are carried out when the data is electronically transferred to the desktop application, where additional editing can be undertaken.
Figure 3: Main RoadMark Android App Screen
Data Storage & Reporting: RoadMark Analysis (RMA)
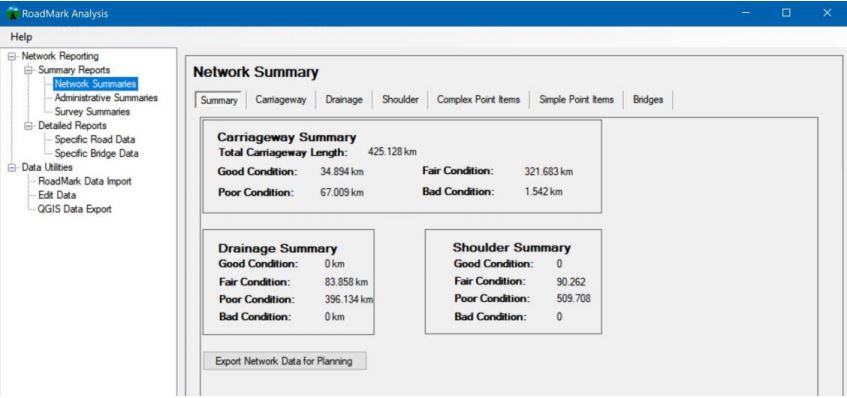
This Windows 10 application allows all survey data to be stored securely in a relational database, from which a variety of reports and data exports can
be generated. Figure 4 shows the main user interface screen for this software.
Figure 4: RoadMark Analysis Network Summary Screen
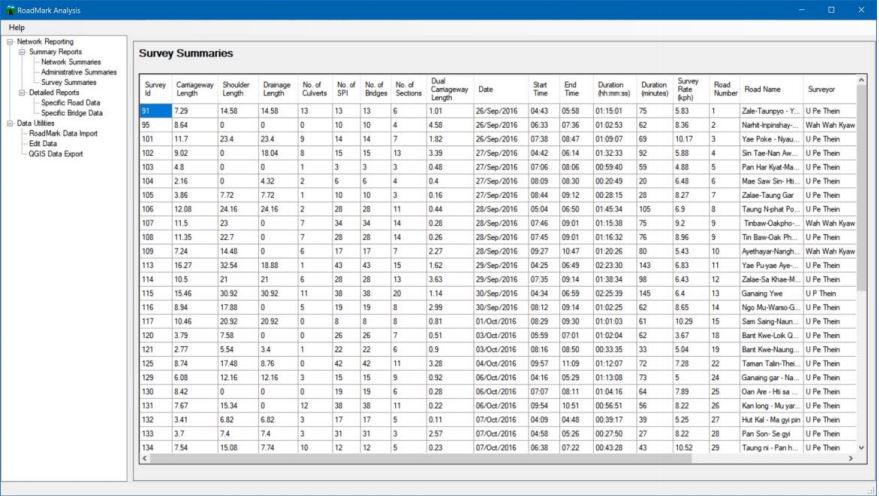
RoadMark Analysis can also provide administrative information about the surveys carried out. This can be useful for monitoring progress, identifying problem
areas and estimating how long (and hence the cost) to undertake future surveys. (See Figure 5.)
Figure 5: Example of Survey Information from RoadMark Analysis
RoadMark Analysis can also provide additional information about specific parts of the network surveyed. An example of this is shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6: Example of Data Recorded in RoadMark Analysis for a Specific Road
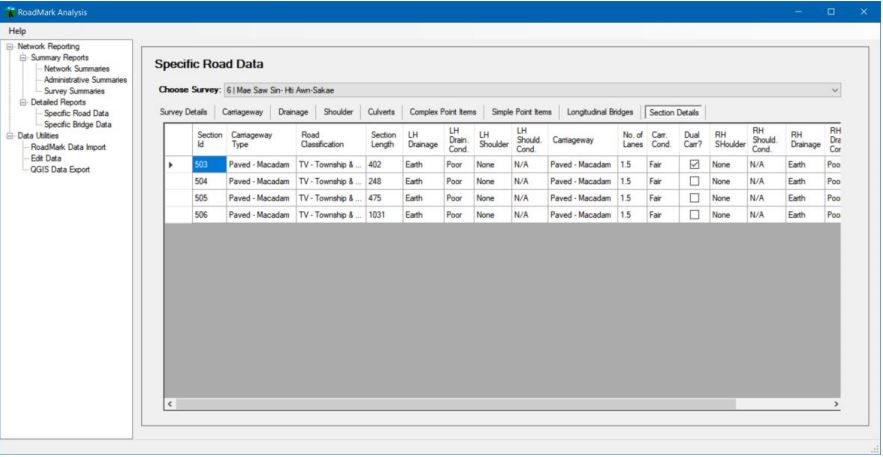
Note: Additional data fields (columns) are available on this form by scrolling right.
Data Export & Use
Data stored in RoadMark Analysis can be easily exported in a format that can be readily used in Excel, other database applications or for reporting purposes.
Network Planning & Budgeting
Figure 7 shows an example of the type of basic planning and budgeting estimates that were developed, based directly on the data collected using RoadMark.
These estimates included both carriageway and off-carriageway estimates, as basic inventory and condition data were collected for non-carriageway assets,
including longitudinal drainage, bridges and culverts.
Figure 7: Example of Network Planning & Budgeting Estimates, based on RoadMark Data
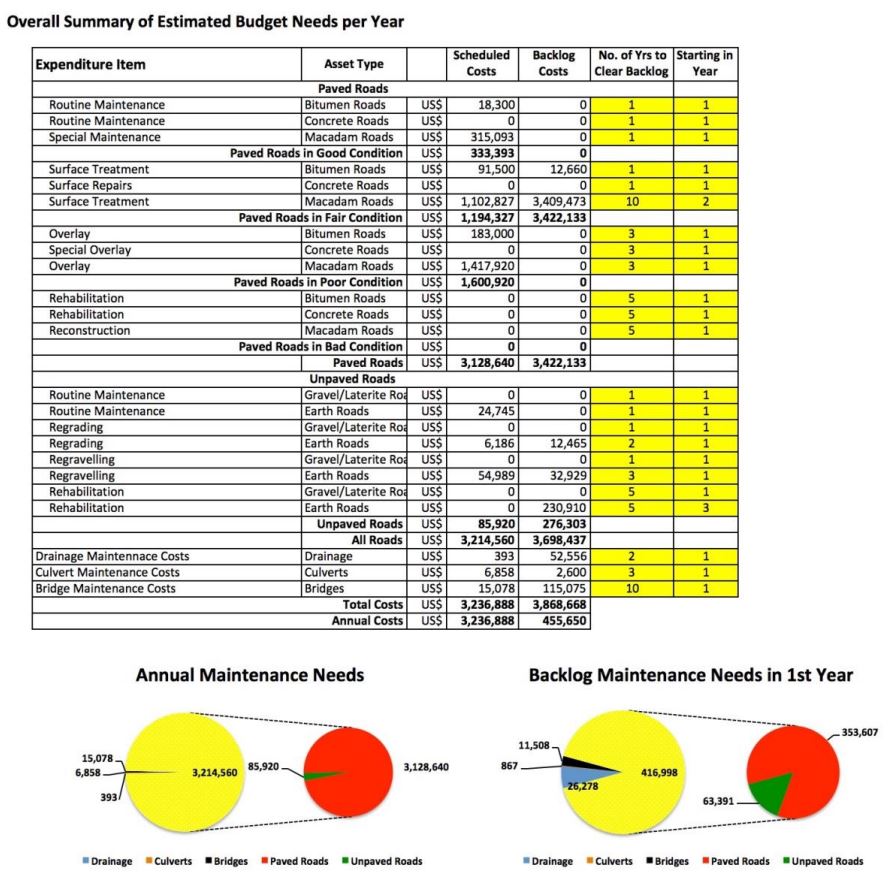
The data from RMA was used in Excel to develop these estimates. This approach allowed easy ‘what-if’ scenario testing to be undertaken, enabling network
managers to quickly understand the impact from changing treatment costs or maintenance standards. This allows limited resources to be targeted on those
parts of the road network where the greatest benefits are likely. Once the data had been collected using RoadMark, and stored using RoadMark Analysis,
this type of analysis required nothing more than readily available software (e.g. Excel), engendering greater ownership and understanding by local
road managers.
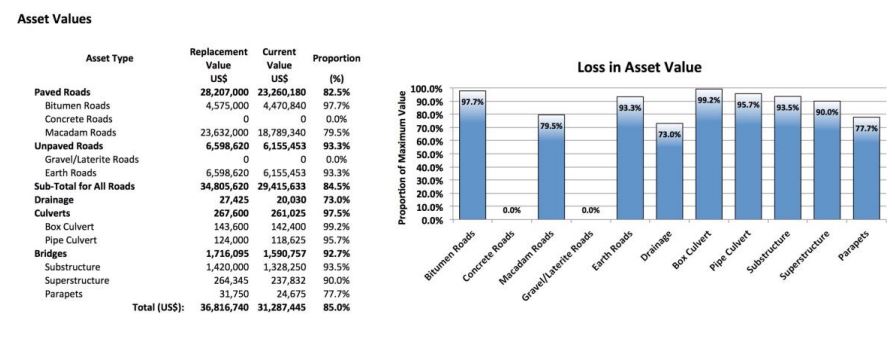
Figure 8: Example of Estimated Road Asset Values Using RoadMark Data
Network Mapping
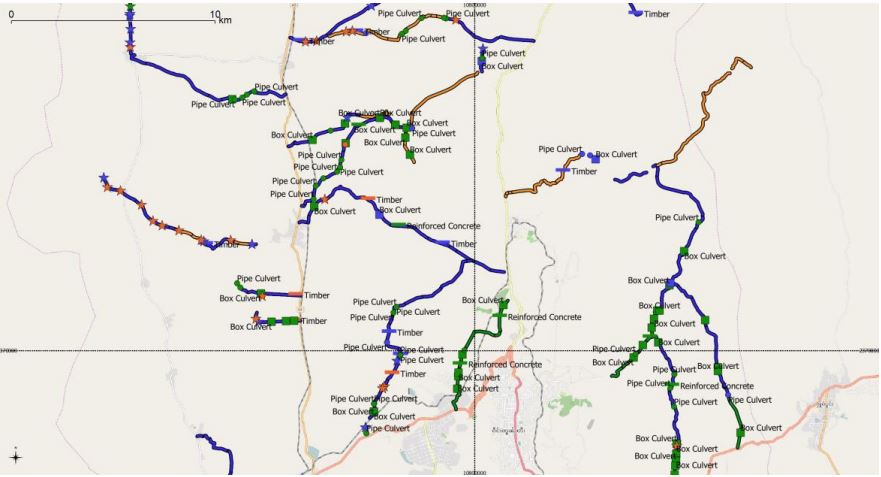
Mapping provides a powerful way of showing important information about a road network, in a format that is readily understandable by non-technical personnel. They are therefore an important tool to explain and support road agencies’ work. Maps are also effective tools for road managers to better understand the road assets under their management.
Because all data recorded by RoadMark is GPS linked, data stored in RMA can be exported in a way that allows maps of the data to be shown, using commonly
used GIS software. Figure 9 shows a map of the roads surveyed, using the freely available, cross-platform QGIS software. This used the data directly
generated by the RoadMark Analysis application. QGIS (and other mapping software) is highly flexible, allowing a wide range of formats and features
to be shown. In this example, road are coloured depending on their pavement condition and the location of any recorded point items (e.g. bridges and
culverts) are also show, coloured depending on their condition. Labels (such as road name and number, or bridge ID numbers or names) can also be turned
on or off for these maps. Background mapping for the area can be obtained from a variety of freely available sources.
Figure 9: Example Map of Road Assets Surveyed using RoadMark
Final Notes
This work was carried out in 2016, since when further developments have been implemented to the RoadMark software, providing greater flexibility, usability and security features, as well as responding to continually changing technological developments.
This case example was developed based on the requirements in Myanmar. However, each country has different needs and capabilities and whilst the RoadMark
software is designed to be simple to use, fast and robust, with over 30 years’ experience in these issues, we would recommend talking to us about your
specific needs and to better understand how the RoadMark software might best match your particular requirements. We employ specialist software developers
to support this software, allowing us to respond to specific requirements as necessary.
This software is developed to be useful for:
| User Groups | Possible Use of RoadMark |
| Road Agencies | To record and store data about their road network assets in a systematic and inexpensive manner. |
| Development Partners | To audit or check the condition and extent of a road network (e.g. for future support and monitoring) |
| Engineering Consultants | To capture the current extent and approximate condition of a part of a road network, quickly and inexpensively, providing data for subsequent analysis, reporting and mapping. |